OSPF LSA Header
(RFC 2328 section 12.1 page 116)
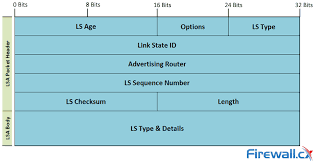
| Field | Bits | Description |
|---|---|---|
| LS Age | 16 | The LS Age field indicates the time in seconds since the LSA was generated. It is essential for assessing the freshness of LSAs and making decisions based on their age, helping routers discard outdated information. |
| Options | 8 | The Options field comprises 8 bits that specify various settings and capabilities. It includes features such as authentication, flooding scope, and more. Routers use these settings to negotiate and understand the OSPF behavior of neighboring routers. |
| LSA Type | 8 | The LSA Type is an 8-bit field that categorizes LSAs into distinct types, such as Router LSA, Network LSA, Summary LSA, and AS-external LSA. Each LSA type serves a specific role within the OSPF protocol, affecting how the LSA information is utilized and propagated. |
| Link-State ID | 32 | The Link-State ID is a 32-bit field that represents a unique identifier for routers or networks associated with the LSA. The format and meaning of this identifier differ based on the LSA type. For instance, in Router LSAs, it signifies the Router ID of the originating router. |
| Advertising Router | 32 | The Advertising Router field consists of 32 bits and contains the Router ID of the router that generated the LSA. This information is crucial for identifying the source of the LSA and determining its trustworthiness. |
| LS Sequence Number | 32 | The LS Sequence Number, spanning 32 bits, is employed to monitor changes within the LSA. It is incremented each time the LSA undergoes modification, enabling routers to identify the most recent version of the LSA. |
| LS Checksum | 16 | The LS Checksum, comprising 16 bits, functions as an error-checking mechanism for the LSA header. It contains a checksum value computed over the header, which assists routers in detecting header corruption or errors that may have occurred during transmission. |
| Length | 16 | The Length field, occupying 16 bits, indicates the overall length of the LSA, encompassing both the header and its content. Routers use this field to locate the end of the LSA, ensuring complete processing without truncation. |

